From 6-14 July 2022, CGIAR Centers in Rwanda, including the International Potato Center (CIP), the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA), the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), , and the Alliance of Bioversity International and CIAT (The Alliance) participated in an Agriculture exhibition, to display its contribution to agriculture transformation through innovative research and policy analysis in Rwanda.
The exhibition is locally dubbed Agrishow and hosted annually by the Ministry of Agriculture and Animal Resource and partners to “foster exchanges in technologies, skills, and best practices between farmers, and other agricultural stakeholders”.
The theme of this year’s Agrishow, “Building Resilience in Agriculture through Modern Technologies,” reflected the aim of Rwanda to leverage digital technologies to fast-track agriculture modernization.
Exhibitors included small and medium enterprises, non-governmental organizations, cooperatives, and research organizations, operating in and supporting agricultural value chains. They exposed innovations in animal resources, crop production, climate adaptation, and digital agriculture that can contribute to the transformation of food systems.
CGIAR centers invest in technological and institutional innovations, partnerships, capacity development, and policy engagement to contribute to Rwanda’s agricultural transformation.

Centers exhibited various innovations in policy analysis, seed systems, capacity development, climate-smart agriculture, digital agriculture, disease and pest control, and circular economy.
The Honorable Minister of Agriculture and Animal Resources, Dr Geraldine Mukeshimana toured the CGIAR stand and commended the centers’ contribution to the agriculture sector.
The Honorable Minister made candid recommendations to advance existing innovations, mainly on Aflasafe development and animal feed production from agricultural residues.” All these innovations are good and important to our community. At scaling, consider the financial capacity of the farmers and set prices accordingly,” she said.

CGIAR centers have been implementing programs in Rwanda since the 1980s. Five centers, namely IITA, World Agroforestry (ICRAF), IFPRI, CIP, and the Alliance maintain a country office, while other Centers such as the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) are also working across a range of collaborative projects and activities in the country.
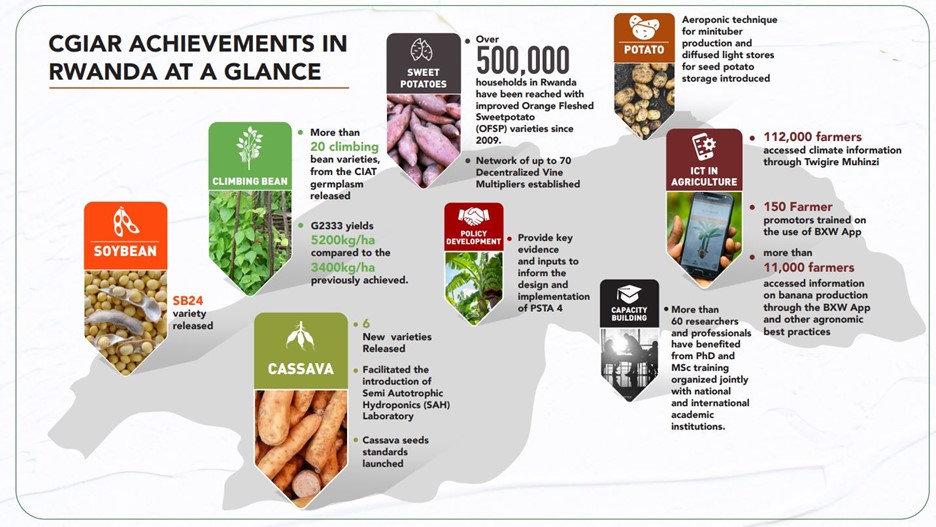
These centers have been operating in Rwanda in complementarity and close collaboration with the Ministry of Agriculture and Animal Resources (MINAGRI), national agricultural research and extension organizations (now primarily the Rwanda Agriculture and Animal Resources Development Board (RAB)), civil society organizations, academia, development partners, and the private sector to conduct and deliver innovative research.


No Comments